Progesterone - The Balancing Hormone
- Progesterone is one of the sex hormones. It plays a role in menstruation, pregnancy, and the formation of embryos.
- Progesterone is made in the ovaries up until menopause. After menopause, it is made in the adrenal glands.
Progesterone is made from pregnenolone and performs many functions in the body:
- Acts as a diuretic
- Is anti-inflammatory
- Aids in ovulation
- Balances estrogen
- Effects the potentiation of GABA
- Enhances the action of thyroid hormones
- Has a positive effect on sleep
- Helps build bone
- Helps maintain bladder function
- Maintains pregnancy
- Helps prevent anxiety, irritability, and mood swings
- Helps restore proper cell-oxygen levels
- Helps the body use and eliminate fats
- Increases metabolic rate
- Increases scalp hair
- Induces conversion of E1 to the inactive E1S form
- Lowers LDL
- Modulates oxytocin receptor binding in the hypothalamus
- Promotes Th2 immunity
- Protects breast health
- Relaxes smooth muscle of the gut to aid in breaking down food
- Supports the immune system
- Helps promote implantation of the egg
- Promotes the formation of myelin sheaths
Symptoms of Progesterone Loss
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Irritability
- Mood swings
- Insomnia
- Pain and inflammation
- Osteoporosis
- Excessive menstruation
- Hypersensitivity
- Nervousness
- Migraine headaches before cycles
- Weight gain
- Decreased libido
- Decreased HDL
Causes of Low Progesterone
- Impaired production
- Low LH
- Increased prolactin production
- Stress
- Antidepressants
- Excessive arginine consumption
- Sugar
- Saturated fat
- Deficiency of vitamins A, B6, C, zinc
- Decreased thyroid hormone
Effects of Too Much Progesterone Even with Adequate Estrogen
- Elevates cortisol
- Increases insulin resistance
- Increases appetite and carbohydrate cravings
- Relaxes the smooth muscles of the gut: can cause bloating, fullness, and constipation. It can also contribute to gallstones.
- Causes incontinence
- Decreases growth hormone
- Causes ligaments to relax and can cause backaches, leg aches, and achy hips
- Suppresses the immune system
Synthetic Progesterone
- Called progestins
- Progestins do not reproduce the same actions of natural progesterone
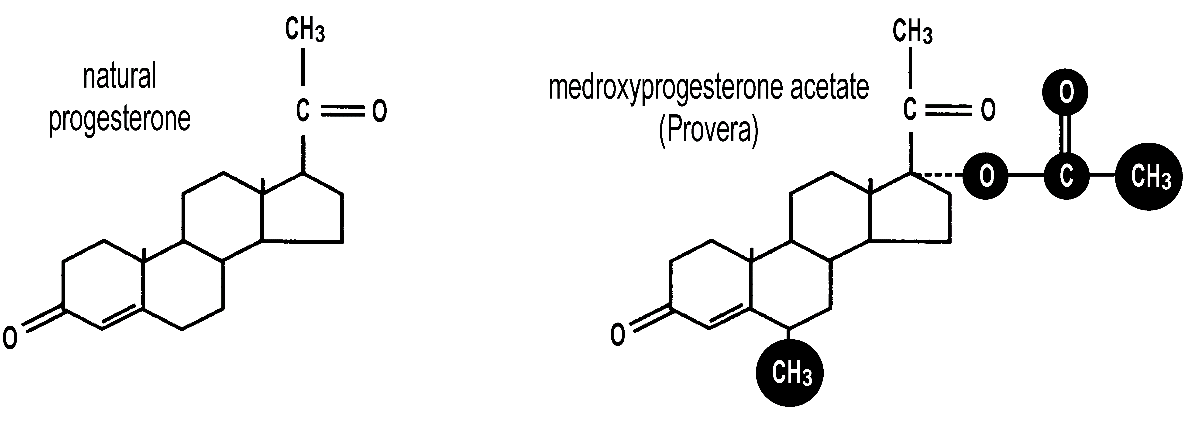
- Pharmaceutical companies cannot hold a patent on natural hormones any more than they can patent air, water, or vitamins.
- But…they CAN structurally change a human progesterone molecule to a synthetic analog or progestin and produce side effects: birth defects, blood clotting, cardiac dysfunction, depression, weight gain, high BP, acne, hirsutism, and breast cancer.
- Wolf Utian, found and former president of the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), misleads women with his statement “If you minimize a woman’s exposure to progesterone, you minimize her slight risk of breast cancer.” Dr Utian is referring to progestin, not progesterone. Progesterone helps prevent breast cancer. It is unfortunate that mainstream doctors still refer to progestins as progesterone-they are completely different.
Side Effects of Progestins
- Increases appetite
- Weight gain
- Fluid retention
- Irritability
- Depression
- Headache
- Decreases energy
- Bloating
- Breast tenderness
- Decreases sexual interest
Side Effects of Progestins
- Acne
- Hair loss
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Interferes with the body’s own production of progesterone
- Does not help balance estrogen
- Remains in the body longer
- Can cause spasm of coronary arteries
- Stop the protective effects estrogen has on the heart
- May make the symptoms of progesterone loss worse
- Increases LDL
- Decreases HDL
- Protects only the uterus from cancer
- Counteracts many of the positive effects of estrogen on serotonin
Natural Progesterone Effects Not Seen with Progestins
- Helps balance estrogen
- Leaves the body quickly
- Improves sleep
- Natural calming effect
- Lowers high blood pressure
- Helps the body use and eliminate fats
- Lowers cholesterol
- Increases scalp hair
- Helps balance fluids in the cells
- Increases the beneficial effects of estrogen on BV
- Increases metabolic rate
- Natural diuretic
- Natural antidepressant
- Is anti-inflammatory
- Stimulates the production of new bone
- Enhances the action of thyroid hormones
- Improves libido
- Helps restore proper cell oxygen levels
- Induces conversion of E1 to the inactive E1S form
- Promotes Th2 immunity
- Is neuroprotective, promoting myelination
More Natural Progesterone Effects Not Seen with Progestins
- Natural progesterone has been shown to decrease the risk of developing breast cancer.
- A study looked at 80,000 postmenopausal women for 8 years using different kinds of HRT.
- It found that women who used estrogen in combination with synthetic progestin had a 69% increased risk of developing breast cancer when compared to women who never took HRT.
- Women who used progesterone in combination with estrogen had no increased risk in developing breast cancer compared to women that did not use HRT and also had a decreased risk in developing breast cancer compared to the women that used progestin.
Reference: Fournier, A., et al., “Unequal risks for breast cancer associated with different hormone replacement therapies: results from the E3N cohort study,” Breast Cancer Res Treat 2008; 107(1):103-11.
Another study done by the same researchers found a 40% increased risk of developing breast cancer in women who used estrogen with progestin.
- In women who used estrogen combined with progesterone there was a trend toward a decreased risk of developing breast cancer.
Fournier, A., et al., “Breast cancer risk in relation to different types of hormone replacement therapy in the E3N-EPIC cohort,” Int Jour Cancer 2005; 114(3):448-54.
Progesterone and Breast Cancer Prevention
- Study measured blood levels of progesterone in almost 6,000 women that were premenopausal.
- Women with the highest levels of progesterone who had regular cycles had a 88% reduction in the risk of developing breast cancer.
Reference: Micheli, A., et al., “Endogenous sex hormones and subsequent breast cancer in premenopausal women,” Int Jour Cancer 2004; 112(2):312-18.
- In another study over 1,000 women were studied for over 30 years who had treatment for infertility. The trial was done to look at subsequent breast cancer risk.
- Women who were deficient in progesterone had 5.4x increased risk of developing premenopausal breast cancer and were10x as likely to die from any cancer.
Cowan, L., et al., “Breast cancer incidence in women with a history of progesterone deficiency,” Amer Jour Epidemiol 1981; 114(2):209-17.
Progesterone References:
Ref: Stein, D., et al., “Does progesterone have neuroprotective properties?” Ann Emer Med 2008; 51(2):164-72.
Prior, J., “Progesterone for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in women,” Climacteric 2018; 21(4):366-74.
Seifert-Klauss, V., “Progesterone and bone: actions promoting bone health in women,” Jour Osteoporosis 2010; 2010:845180.
Neubauer, H., et al., “Overexpression of progesterone receptor membrane component 1: possible mechanism for increased breast cancer risk with norethisterone in hormone therapy,” Menopause 2013; 20(5):504-10.
Murkes, D., et al., “Percutaneous estradiol/oral micronized progesterone has less-adverse effects and different gene regulations than oral conjugated equine estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate in the breast of healthy women in vivo,” Gynecol Endocrinol 2012; 28(Suppl 2):12-5.
Chang, K., et al., “Influences of percutaneous administration of estradiol and progesterone on human breast epithelial cell cycle in vivo,” Fertil Steril 1995; 63(4):785-91.
Foidart, J., et al., “Estradiol and progesterone regulate the proliferation of human breast epithelial cells,” Fertil Steril 1998; 69(5):963-69.
Mueck, A., et al., “Comparison of the proliferative effects of estradiol and conjugated equine estrogens on human breast cancer cells and impact of continuous combined progestogen addiction,” Climacteric 2003; 6(3):221-27.
